What Is E-Invoice? Know All About E-Invoicing Under GST
Recent Updates on e-Invoicing:
10th May 2023
In accordance with the government's aim to shift towards a digital economy, the CBIC has announced the introduction of the 6th phase of e-invoicing. Effective from August 1st, 2023, businesses with a turnover of ₹5 crore or more in any financial year since 2017-18 will be obligated to generate e-invoices.
What is e-invoice?
An e-invoice, also known as an electronic invoice, is a digital type of a traditional paper invoice that records financial transactions among the buyer and a seller. E-invoices typically include the same information as paper invoices, such as the details of the goods or services sold, the prices, and the taxes. They are created, transmitted, and stored electronically, which allows for faster and more efficient processing and reduces the need for physical paperwork.
E-invoices are becoming increasingly popular, particularly in the context of government-mandated systems, such as the e-invoicing system under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India.
What is E-Invoicing Under GST?
E-Invoicing under GST is a system for creating, transmitting, and receiving electronic invoices for goods and services that are subject to the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India, known as GST e-invoice.
What is GST e-invoice?
GST e-invoice is an electronic invoice that is used to record financial transactions related to the goods and services tax (GST) in India. A e-invoice GST replaces the conventional invoicing process and minimises the need for physical paperwork. A GST e-invoice is intended to improve compliance and reduce fraud by streamlining the process of recording GST transactions.
The GST e-invoice includes information such as the invoice number, the GSTIN number of the supplier, the GSTIN number of the recipient, the HSN code of the goods or services, and the GST amount. This information in the e-invoice GST is generated and sent by the supplier to the GSTN (Goods and Services Tax Network) and then received by the recipient through the GST common portal, where they can download and use it for their GST return filing.
Why is e-invoicing introduced?
GST e-invoices aims to streamline the process of generating, transmitting, and receiving invoices by replacing the traditional invoicing system with a digital one. The main reasons e-invoicing is introduced are as follows:
- Improved compliance
- Reduced fraud
- Streamlined process
- Better data analysis
- Improved efficiency
- Better tracking
When Is E-invoicing Required?
The CBIC has announced the launch of the 6th phase of e-invoicing, aligning with the Indian Government's objective of promoting digitalization. From August 1st, 2023, businesses with an annual turnover of ₹5 crore or more since 2017-18 will be mandated to generate e-invoices. This significant initiative is aimed at simplifying the invoicing process, minimizing errors, and enhancing tax compliance, eventually leading to a more efficient and transparent economy.
It should be noted that e-invoicing became mandatory for businesses with a turnover of over Rs. 100 crores from January 1st, 2020, after its introduction in India on October 1st, 2020. Although companies with a turnover of less than Rs. 100 crores are not currently obligated to utilize e-invoicing, they are encouraged to adopt it voluntarily. This latest development is part of the government's ongoing efforts to drive digital transformation in the country, and it is anticipated to impact a significant number of businesses in India.
What is e-invoice limit?
An e-invoice limit refers to the maximum amount that can be billed or invoiced electronically. A GST e-invoice limit can differ depending on the country or regulatory body. In some cases, there may be different GST e-invoice limits for different types of transactions or businesses. In general, the purpose of GST e-invoice limits is to prevent fraud and ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations.
How does a GST e-invoice software help with e-invoicing?
A GST e-invoice software is a program that is used to create, manage, and submit e-invoices that comply with the GST (Goods and Services Tax) laws and regulations in India. GST e-invoice software allows businesses to generate GST-compliant invoices electronically, which can then be shared with customers and submitted to the GSTN (Goods and Services Tax Network) for tax compliance purposes. Some features of GST e-invoice software include:
- Automated calculation of GST taxes
- Ability to generate and download GST invoices in a specified format
- Support for multiple GST rates and taxes
- Integrated accounting and inventory management system
- Validation and error-checking for GST compliance
- Secure and encrypted transmission of invoices to GSTN portal
Using a GST e-invoice software can help businesses to streamline their invoicing processes and ensure compliance with GST laws and regulations, reducing the risk of errors and penalties.
Read Useful Article
Understand The Current System Of E-Invoicing In India
It is necessary to create and report the seller's invoice to the GST Portal and e-Way Bill.Taxpayers typically create invoices using a variety of applications, depending on what is available and enter the invoice information using a compatible API in a GSTR-1 return.
The same data is subsequently reflected in the GSTR-2A, which recipients with "see only" authorization can access. Transporters must simultaneously produce the e-Way Bill, either directly or by manually adding the invoices to an excel sheet or JSON file.
The GST Council in India introduced the new GST return filing mechanism, i.e. e-invoicing in India, to reduce this never-ending paper trail and end this procedure.
Read Useful Article
Applicability of E-Invoicing System
The GST Council introduced the E-Invoicing system (Electronic invoicing system) during its 35th meeting, and a standard e-invoice format was agreed upon during the 37th meeting on September 20, 2019. Since April 1, 2020, businesses with a turnover exceeding Rs. 100 crores are required to issue e-invoices, and B2B invoices must be recorded in the GST System using an electronic invoicing system.
Initially, the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) set the threshold for e-invoicing at 10 crores or more, but it has now been reduced to 5 crores to further encourage a shift towards a digital economy. As part of this effort, the CBIC has announced the 6th phase of e-invoicing, which mandates businesses with a turnover of ₹5 crore or more in any financial year from 2017-18 to issue e-invoices starting from August 1, 2023.
The GST Council has already taken measures to gradually roll out e-invoicing and intends to bring all businesses with a turnover of more than 1 crore within the framework by lowering the annual threshold for e-invoicing from 10 crores to 5 crores. This initiative is just one of many steps the government has taken to promote a digital economy.
Mandatory Parameters For E-invoicing
The mandatory parameters for eInvoicing are:
- Transactional information, such as tax and supplier type
- Document type, number, and date information
- Information about the supplier, including GSTN address, legal name, location, state code, and PIN code
- Identifiers for the buyer, such as the GSTN address, legal name, location, state code, and PIN code
- Dispatch information for address (mandatory in case it is different from the address of address
- Shipping information (mandatory in case it is different from the address of address)
- Details about the item, such as the service or good, the assessable amount, the HSN code, the total amount, the GST rate, and the item's total value
- If the objects are being relocated in batches, the batch number
- Details of the invoice, including the total amount due and the assessable values.
How to Generate E-Invoice Unique IRN?
The GSTIN, document type (regular B2B invoice, export, or credit/debit note), document number, and seller's financial year must all be included in the IRN. The mentioned information will be used by the IRP to build a hash parameter.
To ensure that the identity document (invoice, etc.) from the same supplier about the same Financial year is not uploaded again, the IRP will then check it from the Central Registry of the GST System.
The IRP will also include a QR code in the invoice's JSON data after checking there are no duplicates and adding its signature. The Invoice Reference Number (IRN) for the e-invoice will be the hash produced by the IRP.
How Can You Update The E-Invoice To The GST System?
The portal checks and authenticates the e-invoice before sending it to the seller, who subsequently receives a digitally signed JSON with a special IRN. The GST and e-Way Bill systems are then given access to the uploaded electronic invoice.
The GSTR-1 for the seller and the GSTR-2A for the buyer will then be updated on the GST site. Details from the GST e-invoice schema, such as "Transporter ID" or "Vehicle number," will be utilized to create an e-Way Bill.
The creation of electronic invoices is prohibited on the GST portal. Only the seller's accounting/billing software and their specific ERP solution can be used for e-invoicing. The invoices that the seller uploads will only be accepted, verified, and digitally signed by the IRP.
Read Useful Article
- E-Invoicing Faqs – Frequently Asked Question & Solution On E-Invoicing
- E-Invoice API FAQs – Answers of Frequently Asked Question on E-Invoice API
Road Ahead for E-Invoicing in India
In the long run, e-invoicing will benefit firms and advance in the digital era.
As all the necessary information related to the invoices will automatically populate the returns, the introduction of the e-Invoice system will automate the tax return filing processes and streamline the GST process, making it simpler for taxpayers to obtain the Input Tax Credit.
The use of an electronic invoicing system will eliminate all data entry-related problems with reconciliation, improve transparency, decrease costs, and speed up payment processing.
Read Useful Article
- Top Benefits of E-Invoicing Software For Your Business
- E-invoicing – Guide On E-Invoicing System In India
- How to Generate Electronic Invoicing (e-Invoicing) in Marg ERP Software
How to Generate E invoice under GST?
Businesses use different software platforms to generate invoices and these invoice details are entered manually in GSTR-1 return form. After filing the GSTR-1 form, the details of the invoice appear in GSTR-2A form in the ‘view-only’ format for the recipients only. On the other side, an e-way bill must be generated by the transporters or consignors. They can simply import the invoices in the form of JSON or Excel manually.
As on October 1, 2020, the process remains unchanged for uploading and generating invoice details under the e-invoicing system. It can be done through API or importing to JSON or Excel, either through a GSP or directly. The data will reflect directly on the GSTR-1 form and e-way bill as well.
When To Generate E-Invoice?
E-invoice will be relevant to your company if your annual revenue exceeds 10 crores, and you must electronically upload all B2B and B2G invoices to the portal. The e-invoice needs to be created in the appropriate format and uploaded to the IRP site. The invoice data will be verified by the IRP portal, and it will then return the file with the IRN and a digitally signed QR code.
According to e-Invoicing regulations, an invoice can only be considered valid if it has an IRN and a QR code that has been verified by the IRP (Invoice Registration Portal) . Every business relies heavily on invoicing, therefore it's essential to have business management software that will enable you to generate e-invoices without disrupting how you now run your company.
Benefits of E-Invoicing under GST
- Bridges a gap and fixes data reconciliation to cut down on mismatch errors under GST.
- Real-time tracking is done by the supplier for the invoices prepared
- One can read e-invoices on a particular program which can be accessed by other people. This way, it helps to reduce the risk of errors.
- One can access input tax credit quickly.
- Automation and back-integration of the process of filing tax returns. The invoice data would be reflected automatically in several returns, especially when you generate an e-way bill Part A.
- Tax authorities don’t have to do surveys or audits as they can get all the details needed at the transaction level.
What is the content of E-Invoicing under GST Applicability?
The e-invoice draft has been made public and released in excel template by GSTN on August 20, 2019. The GST Council has approved the same with some changes on September 20 2019, at the 37th meeting by the GST Council. In association with ICAI, the GSTN has drafted the format in compliance with Indian tax laws and GST. The format follows several industry standards and international norms. An individual format caters to several businesses and industries and it looks complete.
Any existing invoice or accounting software vendor like Marg ERP should comply with PEPPOL (Pan European Public Procurement Online) guidelines to generate invoices. Hence, taxpayers can generate an invoice as per the source. The PEPPOL has been referred to as the UBL version of XML by the GSTN.
PEPPOL is the most common standard worldwide these days. The system is backed by several trading communities and business applications for the exchange of information in supply chains with a standard or common format. An individual data entry point is enabled in e-commerce for business. Later on, the flow of data is happening in various portals through IRP.
Here are some of the important parts of e-invoicing by GSTN:
- Masters – It consists of inputs for specific fields given by GSTN, such as State Code, UQC, supply type, invoice type, etc.
- E-Invoice Schema – It has the description of each field, name of the technical field, sample values, whether it is recommended or not, as well as explanatory notes.
- E-invoice template – According to GST rules, this template allows readers to tally the terms they have used in other sheets. Optional fields have been marked yellow and mandatory are green
How to Implement E-Invoice under GST System?
Starting from January 7, 2020, taxpayers with an annual turnover exceeding Rs. 500 crores could generate e-invoices manually using APIs, while taxpayers with a turnover from Rs. 1 crore to Rs. 500 crores could start generating e-invoices from February 1, 2020. From April 1, 2020, e-invoicing became mandatory for all taxpayers, except for those with a turnover of over Rs. 500 crores, whose deadline was extended to October 1, 2020. It is important to note that the aggregate turnover includes the total turnover under one PAN in all GSTINs in India.
To further promote a digital economy, the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) has recently announced the 6th phase of e-invoicing. This mandates businesses with a turnover of ₹5 crore or more in any financial year from 2017-18 to issue e-invoices starting from August 1, 2023. This is one of several initiatives taken by the government to encourage a digital economy.
For Whom E Invoice Is Mandatory?
As of May 10, 2023, e-invoicing is mandatory for businesses with an annual turnover of more than Rs. 5 crores. This means that all businesses with a turnover of more than Rs. 5 crores must generate and upload e-invoices for all B2B and B2G transactions. E-invoicing is a government initiative aimed at improving the efficiency of the GST system and reducing tax evasion.
There are a few exceptions to the e-invoicing requirement. For example, e-invoicing is not mandatory for businesses that are registered under the Composition Scheme or the Non-Resident Taxable Person (NRTP) Scheme. Additionally, e-invoicing is not mandatory for businesses that are in remote areas or that have a low volume of transactions.
Businesses that are required to generate e-invoices can do so through the GSTN portal. The GSTN portal is a government-run website that provides several services to businesses, including e-invoicing. To generate an e-invoice, businesses will need to create an account on the GSTN portal and provide some basic information about their business. Once an account has been created, businesses can start generating e-invoices.
E-invoicing is a relatively new requirement, but it is important for businesses to comply with it. By generating and uploading e-invoices, businesses can help to improve the efficiency of the GST system and reduce tax evasion.
Here are some of the benefits of e-invoicing:
- It can help to reduce tax evasion.
- It can improve the efficiency of the GST system.
- It can provide businesses with better data insights.
- It can make it easier for businesses to track their inventory.
- It can help businesses to comply with GST regulations.
If you are a business with an annual turnover of more than Rs. 5 crores, you are required to generate and upload e-invoices for all B2B and B2G transactions. You can do this through the GSTN portal.
Read other Useful Articles
- GST e-Invoicing Mandatory For Businesses With Turnover Rs. 5 Crores
- e-Invoicing is Mandatory On 10 Crore Turnover for B2B Businesses in India
- e-Invoicing is Mandatory On 20 Crore Turnover for B2B Businesses in India
When Will E-invoicing Be introduced?
Electronic invoicing, or e-invoicing, was introduced in India on October 1, 2020, as a mandatory system for businesses with an aggregate turnover exceeding Rs. 500 crores to generate and transmit invoices electronically. Since then, the government has been gradually expanding the scope of e-invoicing to cover more businesses.
The latest update on e-invoicing is that the government has notified the 6th phase of e-invoicing, requiring taxpayers with a turnover of ₹5 crore or more in any financial year from 2017-18 to issue e-invoices starting from August 1, 2023.
Type Of Business To Whom Is E-Invoice Applicable?
All businesses with a turnover of Rs. 5 crore or more in any financial year from 2017-18 are required to comply with e-invoicing regulations. This mandate applies not only to businesses registered under the GST law but also to unregistered businesses that supply goods or services to registered businesses.
Who Need Not Comply With E-Invoicing?
Apart from the turnover e-invoicing shall not apply to the following categories of registered persons as per CBIC notification no.13/2020:
- A bank, an NBFC, an insurance business, or another financial institution.
- A registered individual offering passenger transport services is referred to as a good transport agency (GTA).
- A registered individual who offers services for admittance to the screening of motion pictures in multiplexes.
- A SEZ unit that has been excluded by CBIC notification no. 61/2020-central tax
- A person who has registered under CGST Rule 14 (OIDAR)
Who Should Upload The E-Invoice?
E-invoice will be relevant to your company if your annual revenue exceeds 5 crores, and you must electronically upload all B2B and B2G invoices to the portal.
What Type Of Documents Are To Be Reported To The GST System?
Apart from all the relevant documents, it includes invoices, bills of supply, delivery challans, credit notes, debit notes, receipts vouchers, payment vouchers, refund vouchers, and e-way bills.
How Is E-Invoice Different From The Current Practice Of Invoicing?
An electronic invoice must be uploaded and authenticated using a unique invoice reference number (IRN) and a digitally signed QR code . Before issuing the invoice to the customer, the seller must print the IRN number and the QR code on it.
It will be simple for businesses utilizing ERP/business management software that seamlessly interfaces with the IRP system and automatically prints the QR code and IRN on the invoice to manage e-invoice requirements without making many modifications to the business process.
What Is The System In Place For Issuing Invoices Before E-Invoicing?
Before e-invoicing, businesses used to generate invoices through various software, and their details were manually uploaded in the GSTR-1 return or using ERP. Once the respective party files the GSTR-1, the invoice information gets reflected in GSTR-2B for the recipients.
What Are The Modes Of Generating E-Invoice?
There are multiple modes of generating e-invoicing, such as
- Web Based- To register or validate an invoice, details can be put into the IRP website.
- API Based- This mode will let all big taxpayers and accounting software providers interact with the invoices registration portal through their software. Like the E-Way Bill system, the IRN can be generated and validated for invoices individually or in bulk.
- SMS Based- Through this mode invoice details can be entered in a specific format and sent to the IRP portal via SMS through processing.
- Mobile App Based- You can also generate e-invoices through the mobile-based app.
- Offline Tool Based- The details of invoices can be entered into the Invoice Registration Portal's website for the registration/validation of the same.
- GSP Based- The GST Suvidha Provider (GSP) is a service taxpayers can use to complete their e-invoice compliance requirements.
How to Raise/Generate E-Invoice under GST?
A taxpayer can raise or generate an E-invoice under GST in the following steps:
- First of all, ensure that the ERP system is used according to PEPPOL guidelines. The taxpayer can set the standard for e-invoicing by working with the software vendor, i.e. e-invoice schema. All the parameters recommended should be notified by CBIC.
- There are basically two options for a taxpayer to generate IRN:
- They can validate the IP address of the system on an e-invoice portal for the integration of API directly or through a GSP.
- Upload the invoices in bulk using a bulk generation tool. It can help generate JSON files that they can upload to generate IRNs on the e-invoice portal.
- Later on, the taxpayer has to raise an invoice on the GST Software . He should provide all the important details like GSTN of supplier, name and address on the bill, item rate, amount of transaction, tax amount, and GST rate.
- After selection of one of those options, raise the invoice on the billing software or ERP software . Later on, upload the invoice details in the fields marked mandatory via GST service provider or ASP, or using JSON file. The IRP will be serving as a central registrar for authentication and e-invoicing. There are different modes to interact with IRP, including mobile apps and SMS.
- All the important details will be validated by the IRP on B2B invoice. The IRP will also look for any duplicate entry and generate IRN as a reference. The IRN can be generated as per four parameters – Invoice Number, seller’s GSTIN, document type in INV/DN/CN format and FY in YYYY-YY format.
- The invoice reference number (IRN) will be generated by the IRP. It will also create QR code and sign the invoice digitally in Output JSON for the supplier. On the flip side, the seller will get notification through email (if given in the invoice) that the e-invoice has been generated.
- The authorized payload will be sent by IRP to the GST portal related to GST returns. In addition, the IRP will forward the details to the e-way bill portal. The same information will be reflected in GSTR-1 for the tax period. The tax liability will be determined in return.
A taxpayer can print his invoice with a logo. All taxpayers have to report only e-invoices in IRP.
How Tax Evasion Can Be Prevented With E-invoicing Under GST System?
Here are some of the ways to curb tax evasion:
- Invoices are less likely to be manipulated as they are generated in advance before transactions.
- Tax authorities can access transactions in real-time. So, the taxpayers have to generate e-invoice through the GST portal.
- Fake GST invoices are less likely to be made and one can claim input tax credit which is genuine because they can generate all invoices using the GST portal. GSTN can easily detect fake claims of the input tax credit as it is tallied with output cred
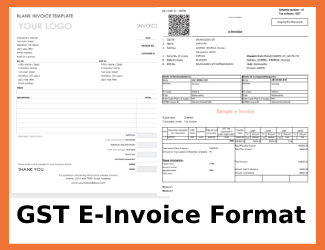
What are the mandatory fields of E-Invoicing under GST?
E-invoices should be made strictly according to the rules related to GST invoicing. In addition, it should also comply with the invoicing policies followed by every sector in the country. You have to fill in some details which are mandatory while some of them are the ones you may or may not fill.
Users can fill up only relevant fields as a lot of fields are optional. There is also a description in all the fields with sample inputs for the users who take an interest. Some fields are sub-supply type in the e-way bill format. Here are the contents in the latest format of e-invoice as on July 30, 2020:
- 12 mandatory and optional sections as well as 6 annexures having 138 fields in total
- 7 are optional fields while 5 are mandatory in 12 sections. Out of 6 annexures, 2 are mandatory.
- Mandatory Sections include Supplier Info, Basic Info, Invoice Item, Recipient details, and Document’s total.
Here are the fields in the e-invoice that should be announced compulsorily:
| Sl. no. | Name of the field | List of Choices/ Specifications/Sample Inputs | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Document Type Code | Enumerated List such as INV/CRN/DBN | Type of document must be specified |
| 2 | Supplier_Legal Name | String Max length: 100 | Legal name of the supplier must be as per the PAN card |
| 3 | Supplier_GSTIN | Max length: 15 Must be alphanumeric | GSTIN of the supplier raising the e-invoice |
| 4 | Supplier_Address | Max length: 100 | Building/Flat no., Road/Street, Locality, etc. of the supplier raising the e-invoice |
| 5 | Supplier_Place | Max length: 50 | Supplier’s location such as city/town/village must be mentioned |
| 6 | Supplier_State_Code | Enumerated list of states | The state must be selected from the latest list given by GSTN |
| 7 | Supplier Pincode | Six digit code | The place (locality/district/state) of the supplier’s locality |
| 8 | Document Number | Max length: 16 Sample can be “ Sa/1/2019” | For unique identification of the invoice, a sequential number is required within the business context, time-frame, operating systems and records of the supplier. No identification scheme is to be used |
| 9 | Preceeding_Invoice_Reference and date | Max length:16 Sample input is “ Sa/1/2019” and “16/11/2020” | Detail of original invoice which is being amended by a subsequent document such as a debit and credit note. It is required to keep future expansion of e-versions of credit notes, debit notes and other documents required under GST |
| 10 | Document Date | String (DD/MM/YYYY) as per the technical field specification | The date when the invoice was issued. However, the format under explanatory notes refers to ‘YYYY-MM-DD’. Further clarity will be required. Document period start and end date must also be specified if selected. |
| 11 | Recipient_ Legal Name | Max length: 100 | The name of the buyer as per the PAN |
| 12 | Recipient’s GSTIN | Max length: 15 | The GSTIN of the buyer to be declared here |
| 13 | Recipient’s Address | Max length: 100 | Building/Flat no., Road/Street, Locality, etc. of the supplier raising the e-invoice |
| 14 | Recipient’s State Code | Enumerated list | The place of supply state code to be selected here |
| 15 | Place_Of_Supply_State_ Code | Enumerated list of states | The state must be selected from the latest list given by GSTN |
| 16 | Pincode | Six digit code | The place (locality/district/state) of the buyer on whom the invoice is raised/ billed to must be declared here if any |
| 17 | Recipient Place | Max length: 100 | Recipient’s location (City/Town/Village) |
| 18 | IRN- Invoice Reference Number | Max length: 64 Sample is ‘a5c12dca8 0e7433217…ba4013 750f2046f229’ | At the time of registration request, this field is left empty by the supplier. Later on, a unique number will be generated by GSTN after uploading the e-invoice on the GSTN portal. An acknowledgement will be sent back to the supplier after the successful acceptance of the e-invoice by the portal. IRN should then be displayed on e-invoice before use. |
| 19 | ShippingTo_GSTIN | Max length: 15 | GSTIN of the buyer himself or the person to whom the particular item is being delivered to |
| 20 | Shipping To_State, Pincode and State code | Max length: 100 for state, 6 digit pincode and enumerated list for code | State pertaining to the place to which the goods and services invoiced were or are delivered |
| 21 | Dispatch From_ Name, Address, Place and Pincode | Max length: 100 each and 6 digit for pincode | Entity’s details (name, and city/town/village) from where goods are dispatched |
| 22 | Is_Service | String (Length: 1) by selecting Y/N | Whether or not supply of service must be mentioned |
| 23 | Supply Type Code | Enumerated list of codes Sample values can be either of B2B/B2C/ SEZWP/S EZWOP/E XP WP/EXP WOP/DE/XP | Code will be used to identify types of supply such as business to business, business to consumer, supply to SEZ/Exports with or without payment, and deemed export. |
| 24 | Item Description | Max length: 300 The sample value is ‘Mobile’ The schema document refers to this as the ‘identification scheme identifier of the Item classification identifier’ | Simply put, the relevant description generally used for the item in the trade. However, more clarity is needed on how it needs to be described for every two or more items belonging to the same HSN code |
| 25 | HSN Code | Max length: 8 | The applicable HSN code for particular goods/service must be entered |
| 26 | Item_Price | Decimal (12,3) Sample value is ‘50’ | The unit price, exclusive of GST, before subtracting item price discount, can not be negative |
| 27 | Assessable Value | Decimal (13,2) Sample value is ‘5000’ | The price of an item, exclusive of GST, after subtracting item price discount. Hence, Gross price (-) Discount = Net price item, if any cash discount is provided at the time of sale |
| 28 | GST Rate | Decimal (3,2) Sample value is ‘5’ | The GST rate represented as a percentage that is applicable to the item being invoiced |
| 29 | IGST Value, CGST Value and SGST Value Separately | Decimal (11,2) Sample value is ‘650.00’ | For each individual item, IGST, CGST and SGST amounts have to be specified |
| 30 | Total Invoice Value | Decimal (11,2) | The total amount of the Invoice with GST. Must be rounded to a maximum of 2 decimals |
E-Invoice Sample Format Under GST System
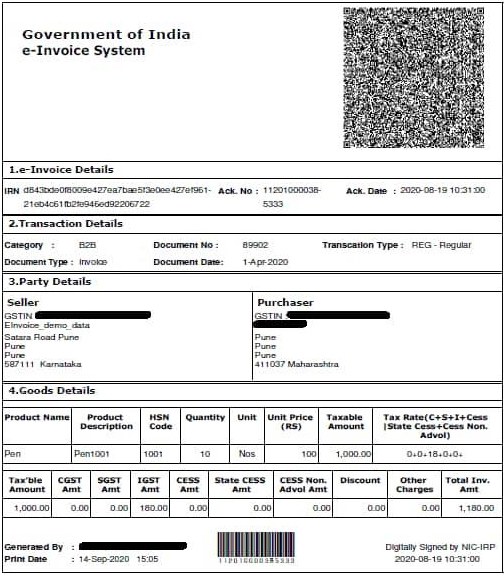
How Do you Download An E-Invoice From The GST Portal?
To download e-invoice data, click on the 'Download Details from e-invoices (excel)' button. The following message will appear on the screen. Now click on the 'E-invoice download history' button to access the downloaded excel files.
What are the penalties for Not Generating E-Invoice and Generating Incorrect E-Invoice?
The penalties for not generating an e-invoice GST or generating an incorrect e-invoice GST can vary depending on the country or region. In general, penalties for non-compliance with e-invoicing laws and regulations can include fines, penalties, and even criminal charges.
In India, the penalties for not generating e-invoice GST or generating incorrect e-invoice GST can include fines, penalties, and even criminal charges. The GST (Goods and Services Tax) act of India has provided for the following penalties for GST E-invoice related non-compliance:
- A penalty of Rs. 25,000 for failing to issue an invoice or issuing an incorrect invoice
- A penalty of Rs. 10,000 for failing to generate an e-invoice or generating an incorrect e-invoice
- A penalty of Rs. 50,000 for failing to upload e-invoice data
- A penalty of Rs. 25,000 for failing to file tax return
What is e-invoice Cancellation?
If an e-invoice GST needs to be cancelled, the e-invoice cancellation process will depend on the specific system or platform being used. In general, the person or company issuing the invoice will need to initiate the e-invoice cancellation process, which may involve contacting the recipient or using a specific tool or feature within the e-invoice system. It is important to check the specific guidelines and rules for e-invoice cancellation to ensure that the process is done correctly and in compliance with any legal or regulatory requirements.
How To Cancel An E-Invoice?
The Procedure For Cancellation Of an E-Invoice Under GST has two steps:
Step- 1 log in to the e-invoice portal and click on the cancel button on the sidebar.
Step- 2 Enter the acknowledgement number on the IRN, then click on Go; now, choose the e-invoice, enter the cancellation reason, and click on submit.
What Is The Time Limit To Cancel E-Invoice?
You can cancel any e-invoice within 24 hours of the IRN's generation. The IRP servers do not store e-invoices for more than 24 hours. Although if an e-way bill is already generated for the IRN, it cannot be cancelled.